Advertisement
What Are The Most Crucial Aspects Of Understanding Ordinary Annuity?
Dec 16, 2024 By Kelly Walker
What Is an Ordinary Annuity? One type of annuity is the "ordinary annuity," which guarantees a certain amount of money at regular intervals (usually monthly, quarterly, or annually) for a set amount of time. It's a way to put money to work that guarantees a specific rate of return in exchange for an initial deposit or ongoing payments. It is an ordinary annuity, as opposed to a due allowance, because payments are made at the end of each month rather than the start. Typical applications for common pensions include retirement savings and other long-term financial objectives. These can be acquired from various economic and insurance providers and come with multiple features, including fixed or variable rates, lifetime income streams, and delayed payment options. Fees, taxes, and penalties for early withdrawals are only a few of the terms and conditions of an ordinary annuity that need to be carefully considered.
The Following Are Characteristics Of An Ordinary Annuity:
How Often And How Long Do You Have To Pay
Most commonly, payments from an ordinary annuity are made monthly, quarterly, or yearly. Payments may be made at regular intervals or over an extended period, depending on the annuity's specific terms and conditions. For instance, one option is to receive regular payments for a set amount of time (say, ten or twenty years) or for the rest of one's life. All annuity payments are based on the initial investment, the interest rate, and the annuity's length.
Interest Rates

An ordinary annuity's interest rate can be either fixed or variable. A fixed-rate annuity is one in which the interest rate is set at the outset and does not change during the annuity's duration. On the other hand, the interest rate of a variable annuity depends on the success of the investments used to fund the contract, such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. Because variable annuity returns are tied to the success of the underlying investments, they are typically riskier than fixed-rate annuities. They carry a greater degree of danger, but due to the possibility of greater reward, they are favored by risk-takers.
Payment Options
Depending on one's needs and interests, an ordinary annuity can be set up in several ways. To illustrate, the assistance can be set up as a single premium immediate annuity. The client pays a single lump amount up front and then receives regular payments for the rest of their lives. Deferred annuities allow the individual to make periodic payments into the pension and start accepting payments at a later date. There are two additional ways to structure an ordinary annuity: a fixed income or a variable payout. The payments from a fixed-income annuity are guaranteed to remain the same throughout the assistance. A variable income annuity, on the other hand, offers payouts that fluctuate with the success of the underlying investments.
Tax Treatment

The regular annuity tax treatment is conditional on the annuity type and the taxpayer's tax status. Payments from an annuity are subject to income taxes at both the federal and state levels since they are considered regular income. Some annuity payouts might be tax-free if the investment was made using post-tax funds. In addition, the development of an annuity is often tax-deferred, meaning that the earnings are only taxed once the annuitant begins receiving payments. Those anticipating a lower tax bracket during retirement may benefit from this strategy.
Conclusion
To receive a set amount of money at regular intervals for a set amount of time, you can purchase an ordinary annuity. It can be a steady source of income for people and businesses, making it an excellent tool for retirement planning and long-term investment goals. Insurance firms and banks offer annuities, and clients can choose from several options to meet their specific needs. Knowing the fine print of an ordinary annuity, such as any associated fees, taxes, and penalties for early withdrawals, is crucial. If a person wants to be sure that their regular allowance fits their financial goals and preferences, they should research and talk to financial consultants. Adding an ordinary annuity to your investment portfolio can provide you with a steady stream of income, potential tax benefits, and peace of mind for the future.
Advertisement

10 Steps to Becoming a Day Trader

What You Need To Know Before Investing in Domain Names?

Understanding Defined Contribution (DC) Plans in Retirement Savings

10 Largest Software Companies
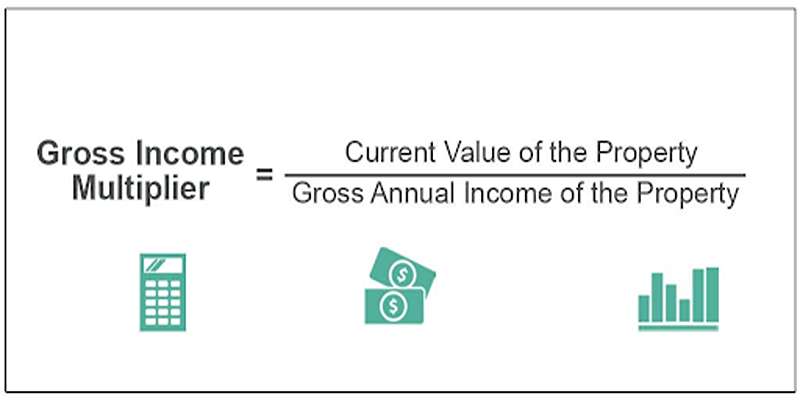
What Is a Gross Income Multiplier?

Are REITs Beneficial During a High-Interest Era?

How much to save in your 20s, 30s, 40s and beyond

Investing in Stock Rights and Warrants

Capital One SavorOne Rewards Credit Card Review

